AWS IAM Users and Permissions for Cloud and DevOps Engineers
Learning path for the AWS Cloud Practitioner exam
📝Introduction
This post will cover the main Technologies of AWS IAM Users and Permissions.
📝AWS IAM Users
Identity and Access Management(IAM) -> It allows you to control access to your AWS services and resources.
Helps you secure your cloud resources
You can define who has access
You can define what they can do
Free global service to use
Shared access to your AWS account
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Identity federation
Granular Permissions
Identity vs Access
Identities -> Who can access your resources
Root user
Individual users
Groups
Roles
Access -> What resources they can access
Policies
AWS managed policies
Customer managed policies
Permissions boundaries
Authentication vs Authorization
Authentication -> It is where you present your identity (username) and provide verification (password)
Authorization -> It determines which services and resources the authenticated identity has access to

Users -> They are entities you create in IAM to represent the person or application needing to access your AWS resources.
Types of Users accounts and what they can do:
Root user -> is created when you first open your AWS account.
Close your account
Change email address
Modify your support plan
Individual users -> They are created in IAM and are used for everyday tasks.
Launch EC2 instances
Configure databases
Perform administrative tasks
Access application code
Note - Don't forget activity performed by users in your account is billed to your account!
Application accounts -> IAM can generate access keys for an application running on-premises that needs access to cloud resources
- Users in the Real World Scenarios:
Create access keys for an IAM user that needs access to the AWS CLI.

Principle of Least Privilege -> It involves giving a user the minimum access required to get the job done.

Groups -> It is a collection of IAM users that helps you apply common access controls to all group members.
Used to group users that perform similar tasks
Access permissions apply to all members of the group
Access is assigned using policies and roles.
i.e Administrators, Developers, Finance
Groups in the Real World Scenarios:
Apply the same access controls to a large set of users and when a user no longer needs access, they can be removed from the group.
Note - Do not confuse security groups for EC2 with IAM groups. EC2 security groups act as firewalls, while IAM groups are collections of users.
📝IAM Permissions
Roles -> They are entities you create and assign specific permissions to that allow trusted identities such as workforce identities and applications to perform actions in AWS.
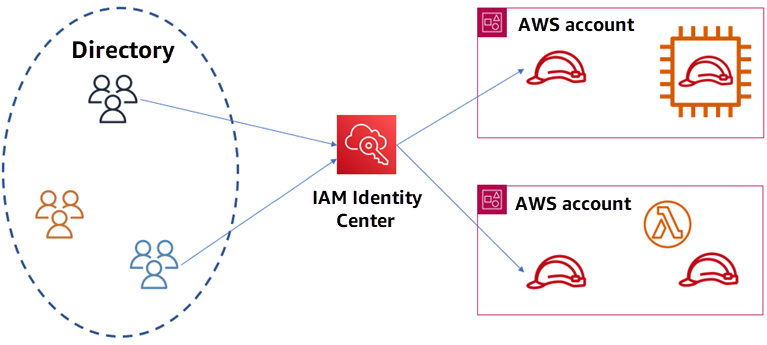
Using IAM roles is a security best practice because roles provide temporary credentials that do not need to be rotated.
Grant access to AWS services
Enable cross-account access
Access workloads that run outside of AWS
Access workloads within AWS
Federate workforce identities into AWS
You assume a role to perform a task in a single session
Assumed by any user or service that needs it
Access is assigned using policies
Roles in the Ral World Scenarios:
Attach a role to an EC2 instance for access to S3 providing privileges (e.g., uploading files to S3) to applications running on the instance. Roles help you avoid sharing long-term credentials like access keys and protect your instances from unauthorized access.

Policies -> To manage permissions for IAM users, groups, and roles by creating
a policy document in
JSONformat and attach it.

Policies in the Real World Scenarios:
To limit access to an Amazon S3 bucket to specific users.

📝IAM Best Practices
There are several recommended best practices for IAM, here are some of them:
Should enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for the root user and other administrative users
Should require IAM users to change their passwords after a specified period of time, prevent users from reusing previous passwords, and rotate security credentials regularly
Shouldn't use the root user for daily tasks
Should use roles for applications that run on EC2 instances instead of long-term credentials like access keys
📝IAM Credential Report
It lists all users in your account and the status of their various credentials.
Also, list the status of passwords, access keys, and MFA devices
Used for auditing and compliance
Thank you for reading. I hope you were able to understand and learn something helpful from my blog.
Please follow me on Hashnode and on LinkedIn franciscojblsouza

